Spring中Bean的生命周期与作用域
Spring中Bean指的就是Spring IOC容器所管理的对象。Spring中的Bean默认都是单例。对于Web应用来说,Web容器对于每个用户创建一个单独的Servlet线程来处理请求,引入Spring框架后,每个人Action都是单例的,Spring的单例是基于BeanFactory,也就是Spring容器的,单例Bean在此容器只有一个。
Bean的作用域
五种作用域。
| 类别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| singleton | 在Spring IOC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例,Bean以单例方式存在,也是默认的配置 |
| prototype | 原型类型,创建容器时没有实例化,每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,即每次调用getBean()时,相当于执行new xxxBean() |
| request | 每次请求Http请求都会创建一个新的Bean,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
| session | 同一个Http Session共享一个Bean,不同Session使用不同的Bean,仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
| globalSession | 一般用于Portlet应用环境,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
五种作用域中有三个是在web应用中使用的,不依赖所用的web容器(tomcat,jetty,undertow etc.)。
使用 @Scope 注解指定 Bean 的作用域。
一般而言,对于有状态的 Bean 应该使用 prototype 作用域,而无状态的应该使用 singleton 作用域。
对于 request 作用域,仅在当前 Http Request 内有效,当请求结束后,该对象的生命周期也结束。
而 session 作用域,每次请求都会生成一个,同时该 Bean 只在当前 Http Session 内有效,与 request 作用域一样。当 Http Session 被废弃时,在该 Http Session 作用域的Bean也会被销毁。
globalSession 的作用域类似标准的 Http session 作用域,不过仅仅在基于 portlet 的 web 应用中才有意义。Portlet 规范定义了全局Session的概念。它被所有构成某个 portlet web 应用的各种不同的 portlet 所共享。在global session 作用域中定义的 bean 被限定于全局portlet Session的生命周期范围内。
Bean的生命周期
Spring容器初始化顺序。
Spring容器初始化开始
调用TestService无参构造函数
TestService中利用set方法设置属性值
执行setBeanName:Bean name defined in context:TestService
执行setBeanClassLoader, ClassLoader Name = jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader
执行setBeanFactory,TestService bean singleton=true
执行setEnvironment
执行setResourceLoader:Resource File Name:spring-beans.xml
执行setApplicationEventPublisher
执行setApplicationContext:: Bean Definition Names=[testService]...
执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,beanName=TestService
执行PostConstruct注解标注的方法
执行InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法
执行配置的init-method
执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,beanName=TestService
Spring容器初始化结束
从容器中获取Bean
Test Name=lgq
执行preDestroy注解标注的方法
执行DisposableBean接口的destroy方法
执行配置的destroy-method
Spring容器关闭
initialization 和 destroy
在Bean属性值set之后和Bean销毁之前可以做一些操作,Spring框架提供了很多方法可以在Spring Bean的生命周期中执行initialization和pre-destroy方法。
实现initializingBean和DisposableBean接口
public class TestService implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行DisposableBean接口的destroy方法");
}
}
但是不建议使用,这样会将Bean的实现和Spring框架耦合在一起。
在Bean的配置文件指定init-method和destroy-method方法
Spring允许创建自己的 init 方法和 destroy 方法,只要在 Bean 的配置文件中指定 init-method 和 destroy-method 的值就可以在 Bean 初始化时和销毁之前执行一些操作。
// 通过<bean>的destroy-method属性指定销毁方法
public void destroyMethod() throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行配置的destroy-method");
}
// 通过<bean>的init-method属性执行销毁方法
public void initMethod() throws Exception{
System.out.println("执行配置的init-method");
}
<bean name="TestService" class="org.lgq.spring.TestService"
init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
</bean>
推荐这种方式,因为这个方式Bean和Spring框架解耦了。
使用@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解
使用@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解,这个两个注解都在javax.annotation下。为了注解生效,需要在配置文件中定义org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor或context:annotation-config
@PostConstruct
public void initPostConstruct() {
System.out.println("执行PostConstruct注解标注的方法");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("执行PreDestroy注解标注的方法");
}
配置文件
<bean
class="org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor"
/>
使用Spring框架的内置对象
通过*Aware接口,可以让Bean获取到一些框架自身的对象。例如通过@Autowired,@Resource注解声明的依赖关系。容器管理的Bean,一般不需要了解容器的状态而直接使用容器,但是在某些情况下,需要在Bean中直接对IOC容器进行操作的,这时候就需要在Bean中设定对容器的感知,SpringIOC容器也提供该功能,通过特定的aware接口来完成。
一些常用的Aware接口
ApplicationContextAware:获得ApplicationContext对象,可以用来获取所有Bean definition的名字。BeanFactoryAware:获取BeanFactory对象,可以用来检测Bean的作用域。ResourceLoaderAware:获得ResourceLoader对象,可以获得classpath中某个文件。ServletContextAware:在一个MVC应用中可以获取ServletContext对象,可以读取context中的参数。ServletConfigAware:在一个MVC应用中可以获取ServletConfig对象,可以读取config中的参数。
public class TestService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, BeanClassLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, EnvironmentAware, ImportAware, ResourceLoaderAware {
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println("执行setBeanClassLoader, ClassLoader Name = " + classLoader.getClass().getName());
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行setBeanFactory,TestService bean singleton=" + beanFactory.isSingleton("TestService"));
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("执行setBeanName:Bean name defined in context:" + name);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行setApplicationContext:Bean Definition Names:" + Arrays.toString(applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()));
}
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
System.out.println("执行setApplicationEventPublisher");
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
System.out.println("执行setEnvironment");
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
var resource = resourceLoader.getResource("classpath:spring-beans.xml");
System.out.println("执行setResourceLoader:Resource File Name:" + resource.getFilename());
}
@Override
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {
System.out.println("执行setImportMetadata");
}
}
BeanPostProcessor
*Aware 接口是针对某个实现接口的Bean定制初始化的过程,Spring同样可以针对容器中所有Bean,或者某些Bean定制初始化过程,实现BeanPostProcessor接口即可。
@Service
public class TestService implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,beanName:" + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization,beanName:" + beanName);
return bean;
}
}
整体流程
- 容器启动后,会对
scope为singleton且非懒加载的bean进行实例化 - Bean容器找到配置文件中的
Spring Bean的定义 - Bean容器利用
Java Reflection API创建Bean实例(循环依赖问题) - 如果有属性值,使用
set方法设置属性值 - 如果实现了
BeanNameAware接口,调用setBeanName()方法,传入 Bean 的名称 - 如果实现了
BeanClassLoaderAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象实例 - 如果实现了
BeanFactoryAware接口,调用setBeanFactory()方法,传入beanFactory对象实例 - 与上面相似,实现了其它
*Aware接口,调用对应的方法 - 如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的
BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法,前置初始化 - 如果使用了
@PostConstruct注解,调用该注解标注的方法 - 如果实现了
InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet()方法 - 如果在配置文件定义了
init-method属性,执行指定的方法 - 如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的
BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,后置初始化 - 当销毁Bean的时候,如果使用了
@PreDestroy注解,调用该注解标注的方法 - 当销毁Bean的时候,如果 Bean 实现了
DisposableBean接口,执行destroy()方法 - 当销毁Bean的时候,如果 Bean 在配置文件定义了
destroy-method属性,执行指定的方法
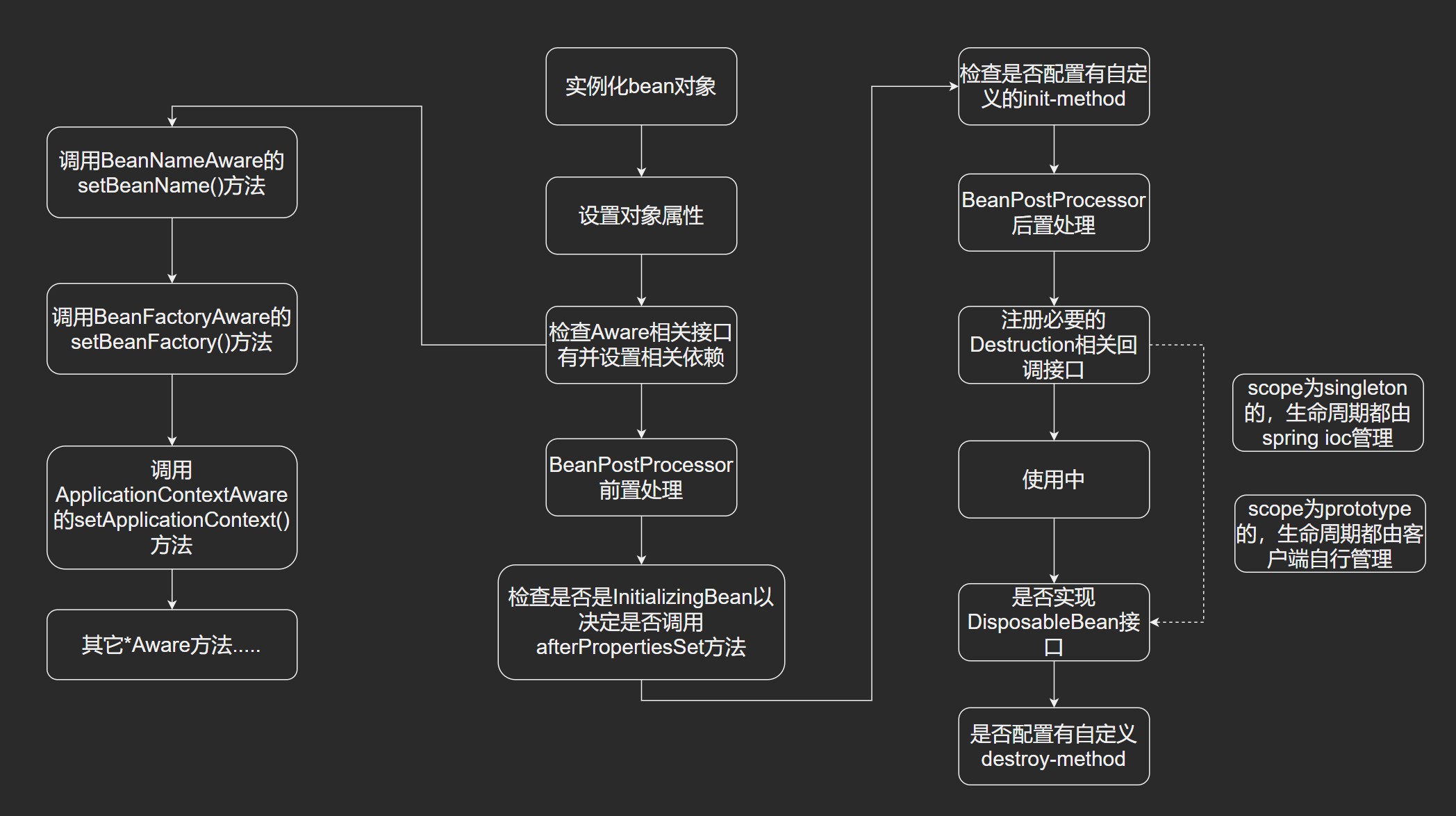
实际开发中,并不会把这些接口都实现,看业务需求。
单例Bean和非单例Bean的生命周期
当scope="singleton",即默认情况下,会在启动容器时(即实例化容器时)时实例化。可以指定Bean节点的lazy-init="true"来延迟初始化bean,这样的话,只有在第一次获取bean时才会初始化bean,即第一次请求获取该bean时才初始化。如下配置
<bean id="TestService" class="org.lgq.service.TestService" lazy-init="true"/>
如果想对所有默认单例bean都应用延迟初始化,在根节点beans设置default-lazy-init属性为true。
<beans default-lazy-init="true"/>
默认情况下,Spring在读取xml文件的时候,就会创建对象。
测试bean代码如下
public class LifeBean {
private String name;
public LifeBean() {
System.out.println("LifeBean构造函数");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("this is init of LifeBean");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("this is destroy of LifeBean" + this);
}
}
life.xml对象配置如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="life" class="org.lgq.spring.LifeBean" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"
lazy-init="true"/>
</beans>
测试代码如下
@Test
public void testLife(){
AbstractApplicationContext container = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("life.xml");
LifeBean life = (LifeBean) container.getBean("life");
System.out.println(life);
container.close();
}
打印日志如下
LifeBean构造函数
this is init of LifeBean
org.lgq.spring.Life Bean@29d89d5d
...
this is destroy of Life Beanorg.lgq.spring.LifeBean@29d89d5d
当scope="prototype"时,容器也会延迟初始化bean,Spring读取xml文件的时候,并不会立刻创建对象,而是在第一次请求该bean时才初始化(如调用getBean方法时)。在请求获取是一个prototype的bean时,Spring容器都会调用其构造器创建新的对象,然后调用init-method属性值中所指定的方法,但是对象销毁的时候,Spring不会调用任何方法,因为是非单例的,对象存在多个的,Spring容器一旦创建对象交给调用者之后,就不会再管理了。
<bean id="life_prototype" class="org.lgq.spring.LifeBean" scope="prototype" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"
lazy-init="true"/>
测试代码
@Test
public void testLife(){
AbstractApplicationContext container = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("life.xml");
LifeBean life = (LifeBean) container.getBean("life_prototype");
System.out.println(life);
container.close();
}
日志如下
LifeBean构造函数
this is init of LifeBean:
org.lgq.spring.LifeBean@5f9b2141
作用域为prototype时,其destroy方法并没有被调用。所以,对于prototype作用域的 bean,有一点非常重要,那就是Spring不会对一个prototype bean的整个生命周期负责:容器在初始化、配置、装饰或者是装配完一个prototype实例后,将它交给客户端,随后不再对该对象进行管理。
不管何种作用域,容器都会调用所有对象的初始化生命周期回调方法。但对prototype而言,任何配置好的析构生命周期回调方法都将不会被调用。清除prototype作用域的对象并释放任何prototype bean所持有的资源,都是客户端代码的职责(让Spring容器释放被prototype作用域bean占用资源的一种可行方式是,通过使用bean的后置处理器,该处理器持有要被清除的bean的引用)。
Spring容器可以管理singleton作用域下bean的生命周期,在此作用域下,Spring能够精确地知道bean何时被创建,何时初始化完成,以及何时被销毁,而对于prototype作用域的bean,Spring只负责创建,当容器创建了bean的实例之后,bean的实例就交给了客户端的代码管理,Spring容器将不再跟踪其生命周期,并且不会管理那些被配置成prototype作用域的bean的生命周期。